- Independent clusters can be added to vastly increase capacity and performance.
Independent clusters share no data and no resources. They can be added with no limit as they perform no inter-cluster communication. Each cluster is accessed through a unique VFS mount point via NFS or CIFS.
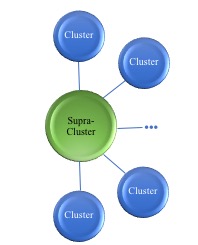
- Clusters can be grouped by the thousands into a Supra-cluster™.
For very large data sets that require hundred or thousands of clients to process (i.e. Hadoop, etc.) a Supra-cluster™ is used to marshall thousands of independent clusters. The Supra-cluster™ disperses the data across all the peers of its clusters. The Supra-cluster is accessed locally through VFS mount points and remotely via NFS and CIFS.
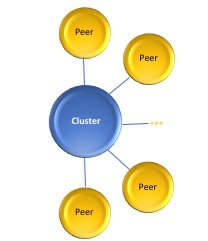
- Additional peers add capacity:
Each new peer adds its storage capacity to the cluster. New files take immediate advantage of the new capacity and existing cluster data can be restriped automatically or manually to use the new capacity.
- Additional peers add I/O, network and CPU bandwidth:
Each new peer adds its I/O, network and computational bandwidth so that data can move faster into and out-of the cluster.
- Additional peers add resiliency:
Each new peer adds to the ability of the cluster to overcome failures. New files take immediate advantage of the added resiliency and existing cluster data can be restriped automatically or manually to benefit from the higher resiliency.
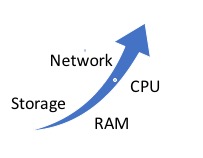
- Improve Processing performance with more RAM and CPUs:
Each new peer adds its storage capacity to the cluster. New files take immediate advantage of the new capacity and existing cluster data can be restriped automatically or manually to use the new capacity.
- Improve Network Performance with more NICs:
Each new peer adds its storage capacity to the cluster. New files take immediate advantage of the new capacity and existing cluster data can be restriped automatically or manually to use the new capacity.
- Improve storage capacity and I/O performance:
Each new peer adds its I/O, network and computational bandwidth so that data can move faster into and out-of the cluster.